Elastography: an innovative technique for assessing coronary artery stiffness
Elastography is a non-invasive imaging method for measuring the elasticity of tissues and organs inaccessible to manual palpation. It involves detecting and measuring the propagation speed of an elastic wave, which is correlated with the hardness of the tissue under study and therefore with the patient’s state of health. This technique is already used to diagnose liver disease or characterize tumors, but could not be used to assess the stiffness of coronary arteries.
Radioelastography: a new approach to assessing coronary artery stiffness
To overcome this limitation, a team from Lyon has developed radio-elastography, a method that uses X-ray radiography to detect the bending wave of the coronary arteries. This wave, which is slower than the pulse wave, can be observed in a single plane thanks to a contrast medium and an algorithm based on the elastic theory of tubes. This technique has been validated on artificial blood vessels and on patients, enabling a stiffness score to be obtained for each individual.
A major advance in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease
Thanks to radio-elastography, doctors will now be able to assess the stiffness of coronary arteries during coronary angiography, an examination commonly used to detect myocardial infarction. This additional information will help refine the diagnosis and adapt patient management, given that artery stiffness is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. This breakthrough was made possible by the discovery of a second pulse wave, known as the “flexion wave”, by the Lyon-based team.
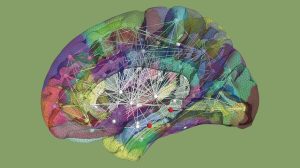
High-resolution reconstruction of a digital brain twin. Cortical and subcortical areas, as well as brain connections, are captured in the form of network nodes and connectivity. The network is then algorithmically transcribed into mathematical equations and simulates the patient’s specific brain activity. INS Marseille
Viktor Jirsa and Fabrice Bartolomei are researchers at theSystems Neuroscience Institute ( Inserm/Aix Marseille University Unit 1106) in Marseille.
Sources :
V. Jirsa et al. Personalised virtual brain models in epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. , online edition March 24, 2023; doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00008-x – F. Missey et al. Non-invasive Temporal Interference Stimulation of the Hippocampus Suppresses Epileptic Biomarkers in Patients with Epilepsy: Biophysical Differences between Kilohertz and Amplitude Modulated Stimulation. medRxiv, preprint January 14, 2025; doi: 10.1101/2024.12.05.24303799
This article has been adapted from content published by Inserm. Find the source article and all references on the Inserm website.